food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome symptoms
The first International Consensus. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion can be 30 minutes to 6 or more.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Page 6 The Fpies Foundation
The hallmark symptom is severe vomiting.
. FPIES is presumed to be cell-mediated. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. It is also called FPIES pronounced like the letter F followed by the word pies FPIES is a rare type of food allergy that affects the digestive tract.
The quality of life for patients and families affected by Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES by means of education research advocacy and support. The symptoms of a reaction. In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy typically presenting in the first year of life. Food proteininduced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy characterized by delayed and often dramatic gastrointestinal symptoms. An acute form and a chronic form.
Acute FPIES reactions include. Unlike most food allergies that produce immediate reactions such as hives swelling and respiratory symptoms FPIES reactions are delayed and usually begin about two hours after ingestion of the trigger food. FPIES is a non-IgE mediated immune reaction in the gastrointestinal system to one or more specific foods commonly characterized by profuse vomiting and diarrhea.
Severe vomiting Diarrhea sometimes bloody Weight loss Dehydration Lack of energy Failure to thrive. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition that occurs in infants and young children although it can rarely affect older children or adults as well. Chronic FPIES is uncommon and usually occurs in infancy due to repeated exposure to a food trigger usually cows milk protein or soy.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different forms. According to the previous international consensus guidelines while digestive symptoms such as vomiting diarrhea and bloody stools are the main symptoms of FPIES approximately 15 of the FPIES patients also. Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion Diarrhea that begins after vomiting Dehydration Severe lethargy Changes in.
Poor growth may occur with continual ingestion. In about 20 percent of cases the child will experience. Ad Find Deals on inflammatory bowel disease supplement in Nutrition on Amazon.
What are acute FPIES symptoms. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES is a food allergy that mostly affects infants and young children. Symptoms such as paleness and lethargy fatigue also may occur.
Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock. Upon removing the problem food s all FPIES symptoms subside.
It typically causes vomiting and bloody diarrhea after consumption of certain foods the trigger foods arent the same for everyone. An FPIES child often looks healthy on the outside. I-FPIES is a worldwide leader in FPIES.
Some children have symptoms that. Symptoms show up a few hours after eating. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in infants.
However this is population dependent and different studies have shown varying. To explore the relationship among gastrointestinal GI symptoms immune response and autonomic nervous system ANS in food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in relation to the current understanding of disease phenotype and pathogenesis. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated food allergy that develops during infancy.
FPIES typically occurs in the first year of life. While the pathophysiology of FPIES is poorly understood the clinical presentation of acute FPEIS reactions has been well characterized. It presents with persistent vomiting andor diarrhoea which can result in poor weight gain over time.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon. Symptoms You may notice that a couple of hours after your baby eats they vomit over and over and then get diarrhea. Acute food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated allergy and is characterized by repetitive profuse vomiting episodes often in association with pallor lethargy and diarrhea presenting within 14 h from the ingestion of a triggering food.
Relevant studies related to FPIES GI symptomatology and ANS were reviewed. Symptoms are primarily gastrointestinal including repetitive vomiting and sometimes diarrhea. Severe reactions can prompt a medical emergency such as dehydration.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome typically affects infants and young children. Patients manifest with symptoms of repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 h of ingesting a food trigger and can also present with pallor and lethargy and diarrhea may present within 510 h. When the syndrome was first described FPIES was thought to affect only infants and to be predominately triggered by cows milk and soy.
Prognosis was good with high rates of resolution for the 2 most common food triggers ie rice and soy by 3 years of age. It is what is going on inside and the cost of.

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

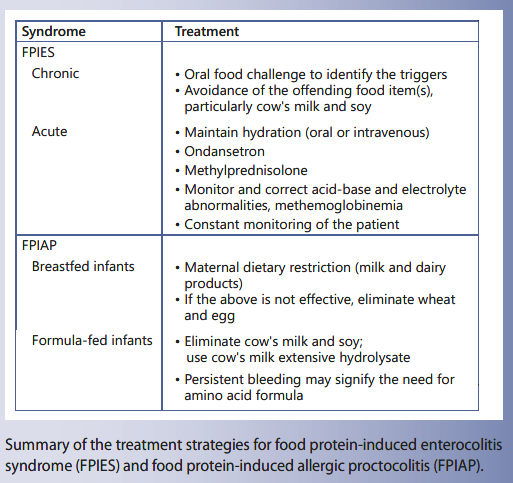
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Treatment
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome As A Cause For Infant Hypotension The Western Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Nourish Little Lives There Are Lots Of Ways That A Food Allergy Can Present In Babies And Children And Not All Reactions Are Obvious And Immediate Fpies Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
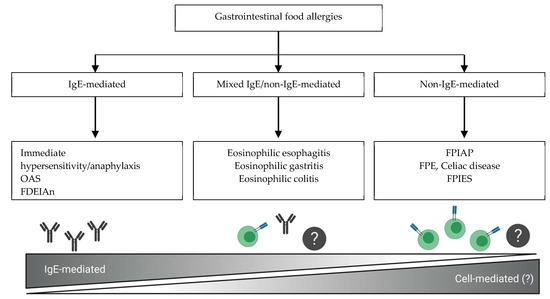
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Description Of Differences And Similarities Between Fpies Fpe And Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison Between Acute And Chronic Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Eastmidsfoamed On Twitter Following Up On Our Fpies Quiz Yesterday We Ve Got A New Lightninglearning All About Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Https T Co Bmzzoug18i Twitter